FLNP JINR researchers conducted air biomonitoring in national park of Kazakhstan
News, 16 September 2024
Researchers from the Laboratory of Neutron Physics at JINR, in cooperation with their colleagues from scientific and educational centres of Georgia, Kazakhstan, Moldova, and Romania determined the air pollution level in the Burabay National Park located in the north of the Republic of Kazakhstan using moss as biomonitors. According to the contamination factor and pollution load indices, the area belongs to three classes of pollution: unpolluted, suspected, and moderate. Calculating the potential ecological risk index for selected elements revealed no harm to human health.
Burabay State National Natural Park is a national park of great natural and historical value. In recent years, it has been exposed to significant anthropogenic impact. The moss biomonitoring was performed in the Borovoye Resort, an important tourist destination of the national park, to identify the air pollution level.
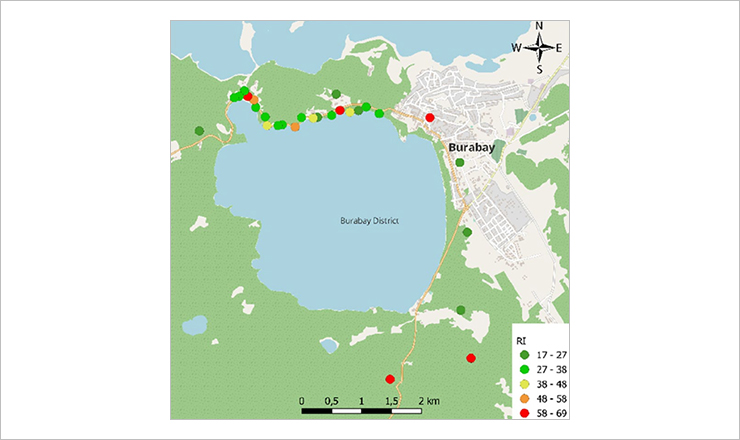 The spatial distribution maps build for ecological risk index in moss samples collected in Burabay State National Natural Park
The spatial distribution maps build for ecological risk index in moss samples collected in Burabay State National Natural Park
Mosses collected at 29 locations were subjected to neutron activation analysis, which determined 36 elements, and to ICP-OES to detect the Cu and Pb levels. Factor analysis was applied to check if there was any associations between identified elements and whether it was possible to link them with potential emission sources. The level of elements in samples from Burabay State National Natural Park was compared with the data available for other national parks.
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment published an article on this research. The team of the authors: Makhabbat Nurkassimova, Nuriya Omarova, Inga Zinicovscaia, Nikita Yushin, and Omari Chaligava.